Digitalization in Africa: Progress, Divide, and Potential for building climate resilience
Context and Investment Insights - Exploring 9 Priority Areas for Climate Action
Hi all,
there’s much talk about the digital leap in Africa - tech startups, and digital innovations like “mobile money” have caught the attention of global software firms and VC investors like.
Digitalization is a key lever for the continent’s sustainable, inclusive growth.
It opens a world of online education, financial services, higher agricultural yields, stronger climate resilience, and so much more.
So today, let’s dive into the last of our deep-dives in this knowledge series on:
#9: Digital transformation

🕐 In a Hurry? Here's a 1-Minute Summary:
Rapid Growth of Digitalization: Sub-Saharan Africa is witnessing a digital boom, with mobile phone ownership reaching 84% and internet usage increasing from 9.6% in 2010 to 33% in 2021.
Persistent Digital Divide: Despite advancements, challenges like unreliable electricity and limited broadband access, especially in rural areas, persist. Significant disparities exist between countries, e.g., in internet usage between Ghana (58%) and the DRC (14%).
Digitalization's Role in Climate Resilience: Digital technologies, including drones, AI, and satellite tech, are revolutionizing sectors like agriculture in Africa, providing critical data for improved farming practices and climate resilience. We’re shining a spotlight on Amini, which is working towards creating a single source of truth for African environmental data.
Significant Market Potential: The internet economy is projected to add $180 billion to Africa's GDP by 2025, with major tech companies like Google and Microsoft investing in African digital infrastructure. It will take around $100 bn in investments to connect all Africans to the internet, and fully take leverage the benefits of digitalization.
Emerging Investment Areas: Promising investment sectors include EdTech, HealthTech, Data Analytics, Data Centers, and Cybersecurity, with significant contributions from Pan-African VC funds and global tech giants. These sectors are crucial for leveraging Africa's digital potential and young demographic.
⏳ Ready for a Deeper Dive? Here's the Breakdown:
Context: Key facts and figures
(1) Digitalization is rapidly advancing in Sub-Saharan Africa
Nearly half of the world's top 40 fastest expanding mobile markets (2021) were located in Africa.
Mobile phone ownership in Africa has increased to 84%, leading to greater access to services like mobile banking and e-commerce.
Alongside this, internet usage has jumped to more than 570 million users, largely driven by mobile connectivity.
Spotlight: Rwanda 🇷🇼
Rwanda is amongst Africa’s frontrunners when it comes to digitalization. The country has substantially invested to achieve 90% broadband internet coverage and three-quarters of its citizens owning mobile phones.
In response to the early challenges of the pandemic, this tech-forward approach enabled Rwanda to launch immediate digital mapping for COVID-19 tracking, expand remote medical consultations to lower physical clinic attendance, and implement automated messaging systems for timely information about the illness.
The country is also developing in a start-up hub in the region.

(2) Significant digital divide prevails
While digitalization is making strides in Africa, it's important to acknowledge the hurdles that are still in place.
One of the key issues is the reliability of electricity supply, which can be quite unpredictable, but essential for any digital operation.
Then there's the matter of broadband access. While urban areas are increasingly well-connected, rural areas often find themselves on the other side of the digital divide.
The same goes for disparities between different countries across the continent. For example, internet usage in Ghana reaches 58%, whereas in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), it stands at just 14%.
And as digital capabilities expand, concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy are climbing up the priority list. This balance between expanding digitalization and maintaining security and privacy is a delicate one, and it's a key part of the conversation about digitalization in Africa.
(3) Digitalization is pivotal in enhancing climate resilience throughout Africa
Despite the challenges, digitalization is playing a transformative role in Africa's economies, not only fostering job creation but also addressing the critical issue of climate change.
Let's take agriculture as an example. Here, cutting-edge digital innovations can revolutionize the way farming is done.
Think about how drones, satellite tech, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and sophisticated devices are being harnessed. Those tools empower farmers with essential data, getting real-time insights on weather patterns, crop health or irrigation needs.
Such data also opens the doors to financial services, including insurance.

Spotlight: Nairobi-based climate tech startup Amini focuses on addressing Africa's environmental data scarcity
Amini employs artificial intelligence and satellite technology to develop a single source of truth for African environmental data.
Such data will help customers in the agricultural insurance sector and in supply chain monitoring, as well as multinational companies seeking to measure their carbon footprint.
The startup has raised significant funding to support its objectives. In a pre-seed funding round, Amini raised $2 million, led by Pale Blue Dot, a European climate-focused venture capital firm. The funding is aimed at launching Amini's first satellite in early 2025, which will improve the collection of Africa-focused environmental information.
The company is planning a constellation of at least six satellites to provide more precise data on various environmental factors such as drought, flood, soil, and crop health over Africa.
Investment insights
(1) Market: Rapidly growing for digital infrastructure, drying up for the tech ecosystem
The IFC and Google project that the internet economy could contribute an additional $180 billion to Africa's GDP by the year 2025.
But to harness the full potential and leverage the skills of Africa’s young population, over a billion new users will need to be connected to affordable and high-quality broadband internet by 2030, requiring an estimated additional $100 billion in investments over the next 10 years.
In recent years, major tech giants have recognized Africa's connectivity gaps and investment needs as significant business opportunities.
Big tech companies, including Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and Amazon, have opened data centers, technology and startup hubs in key African markets like South Africa, Nigeria, Egypt, and Kenya.
Investments in African data centers are boosting the continent's hosting capacity with services like cloud computing and storage. Since 2019, the African cloud market has doubled and is growing annually by 25 to 30 percent. It's anticipated that over 70 percent of businesses across Africa will adopt cloud-based services within the next years.
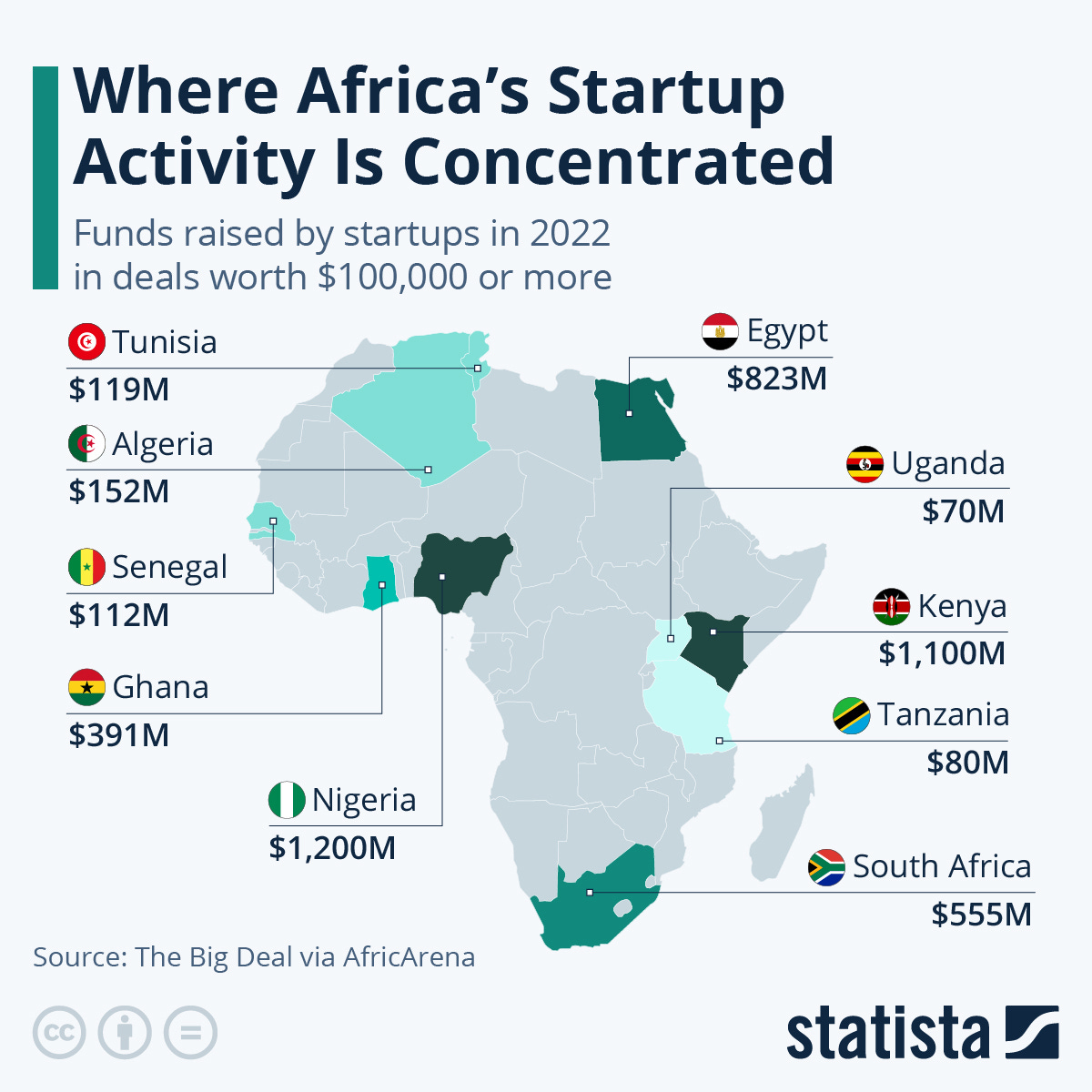
African startups, particularly in fintech, e-commerce, and agritech, have attracted significant venture capital investment, with amounts rising from $186 million in 2015 to $3.3 billion in 2022. Significant hubs are in Nigeria, Kenya, Egypt and South Africa.
Yet, in 2023, there has been a noticeable decrease in funding for Africa's startup ecosystem. This has raised concerns that without adequate follow-up investments, many young companies might struggle to survive and achieve global competitiveness, potentially leading to stagnation in the sector.
(2) 5 Investment areas we’re excited about
EdTech: Digital education platforms, e-learning tools, and companies creating content tailored to African educational systems.
HealthTech: Digital health solutions, telemedicine, and health information systems that improve healthcare delivery and access.
Data Analytics and Transparency: Companies that specialize in collecting, compiling, and integrating data to enhance transparency.
Data Centers and Cloud Services: Companies building or operating data storage and cloud computing services.
Cybersecurity Solutions: Companies that provide cybersecurity services and training.
(3) Investors leading the way - selected examples
Pan-African VC funds investing into tech startups such as Launch Africa Ventures, Seedstars Africa Ventures, and Norrsken22, and many more
Tech giants like Amazon, Google and Microsoft
Accelerators like MEST Africa, Future Africa and Techstars
Sources to learn more:
The Worldbank’s Digital Economy for Africa Initiative
The rise of Africa’s digital economy by the European Investment Bank
e-Conomy Africa 2020 - Africa’s $180 Billion Internet Economy Future by the IFC and Google
Enjoying out content?
Don’t keep it for yourself and share!
Subscribe to not miss future updates!
Feedback or thoughts?
Please let us know! Just reply to this e-mail. We’re happy to hear from you!
Thanks for reading,
Carolin
Disclaimer: All information provided is not intended to serve as investment advice. Any mention of industries or countries should not be taken as an endorsement.

