Direct Air Capture: Unlocking Carbon Removal Potential in Sub-Saharan Africa?
3 reasons for further exploration
What is Direct Air Capture (DAC)?
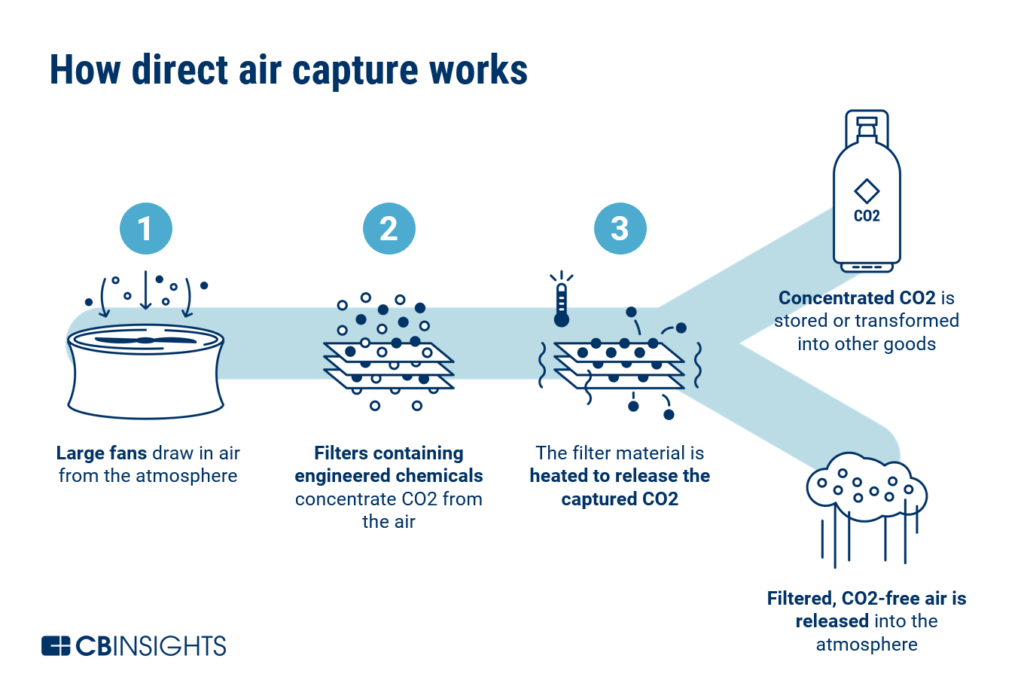
DAC is a revolutionary technology designed to remove CO2 directly from the atmosphere. Highly simplified, the process involves three main steps:
Air Capture: Large fans draw in air, which comes into contact with a chemical sorbent or solvent that selectively absorbs CO2 from the air. Specialized filters or adsorbent materials facilitate this process.
CO2 Separation: After capturing CO2 from the air, the sorbent is processed to release the CO2 from it. Heat or other methods are commonly used for this step, resulting in a purified stream of CO2.
CO2 Storage or Utilization: The captured CO2 can either be stored underground in geological formations (carbon sequestration) or put to various applications, such as enhanced oil recovery or in the production of materials and fuels.
Key Advantages
🌍 Location Independence: CO2 can be removed from the air anywhere, regardless of where it was originally emitted.
🏞️ Small Footprint: DAC facilities can be located in non-arable land, minimizing the impact on valuable agricultural areas.
🌬️ Direct reduction of Atmospheric CO2: The name already says it - by directly removing CO2, DAC actively contributes to mitigating the effects of climate change.
Challenges
💡 Energy Intensive: The process of air circulation and CO2 separation requires significant amounts of power, which can have environmental implications if the energy is not derived from renewable sources.
💸 High Cost: Currently, DAC is the most expensive method of carbon capture compared to capturing CO2 at its emission source. The IPCC report cites a cost range of DACCS between USD 100 to 300 per ton of CO2.
The current status and ambition
Currently, there are 27 DAC plants commissioned across Europe, North America, and the Middle East, capturing approximately 0.01 Mt CO2 per year. However, the International Energy Agency (IEA) envisions a Net Zero Emissions Scenario that requires the removal of 75 Mt CO2 annually.
CO2 capture by direct air capture, planned projects and in the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, 2020-2030

Potential for Sub-Saharan Africa: 3 reasons for further exploration
Direct Air Capture seems promising as a technology to help fight against climate change. 3 reasons that make it an interesting avenue for further exploration and potential investments from my point of view:
☀️🌬️💧 Abundant Renewable Energy Resources: The region is strategically positioned with access to ample renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, which can offset the energy-intensive requirements of DAC.
🏞️🌍 Access to Remote Areas: Africa has extensive non-arable land and remote areas where DAC facilities could be located without negatively impacting valuable agricultural lands.
🚀 Unexplored Capacity: Approximately 60% of the DAC capacity announced for 2030 is currently in early development stages and has not been assigned specific locations yet. Project developers are waiting for favorable regulations before finalizing their expansion plans.

